5-Minute Fundamentals: Introduction to HTML Syntax
 Welcome to a voyage into the fascinating world of HTML or Hypertext Markup Language. HTML is not just a series of arbitrary characters, but a rich language that is the cornerstone of the web. More akin to a templating language rather than a standard programming language, HTML imparts structure rather than logic. This post will serve as an in-depth primer on the essential stuff you need to start on the path of web development.
Welcome to a voyage into the fascinating world of HTML or Hypertext Markup Language. HTML is not just a series of arbitrary characters, but a rich language that is the cornerstone of the web. More akin to a templating language rather than a standard programming language, HTML imparts structure rather than logic. This post will serve as an in-depth primer on the essential stuff you need to start on the path of web development.
What is HTML
HTML forms the primary structure that web browsers use to present the content of web pages which makes HTML coding an ideal stepping stone into the broader programming universe.
“HTML is perhaps better thought of as a templating language because while it doesn’t convey logic, it does convey structure.”
One characteristic feature you will encounter when dealing with HTML is the way it pairs tags. HTML is typically composed of pairs of tags, which contain further nested pairs of tags. Just tags, all the way down.
Each tag, both opening and closing, without exceptions, is encapsulated within angle brackets < and >. However, some notable exceptions to the pairing rule do exist. For example, in certain tags like <!DOCTYPE>.
 ## HTML Tags
## HTML Tags
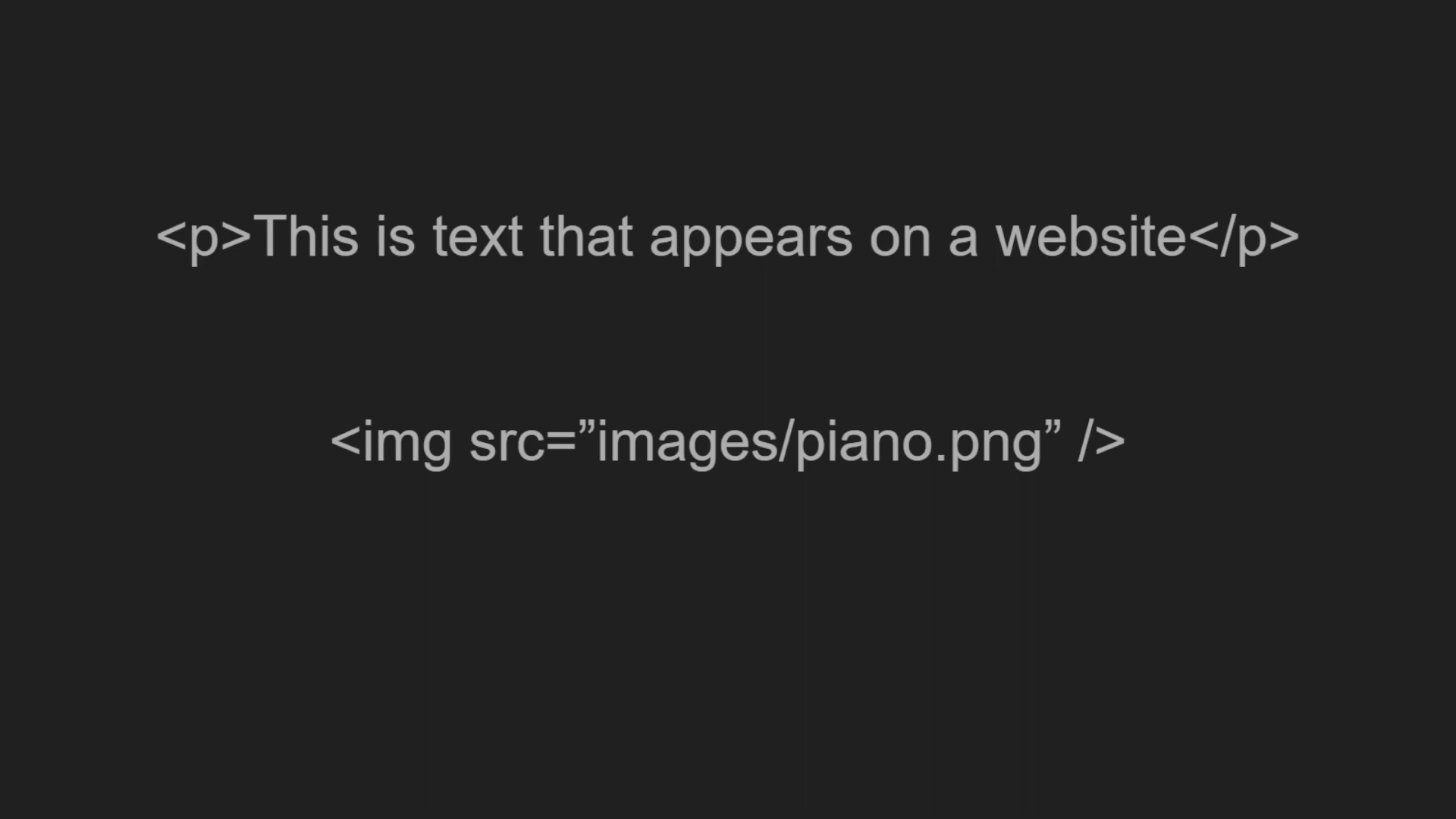
Next, let’s delve deeper into HTML tags. These tags are often classified based on the type of content they hold. For instance, paragraph tags <p></p> hold textual data, image tags <img> encapsulate images.
One outstanding feature of the HTML tags is their ability to nest other tags. Building HTML templates, the HTML basis of any given webpage, requires the nesting of tag pairs within others in a structured manner.
HTML Attributes
Moving on, HTML also comprises attributes, another vital aspect of the language. For example, an image tag <img> might contain a src attribute providing the necessary information for the image display.
 ## Essential HTML Tags
## Essential HTML Tags
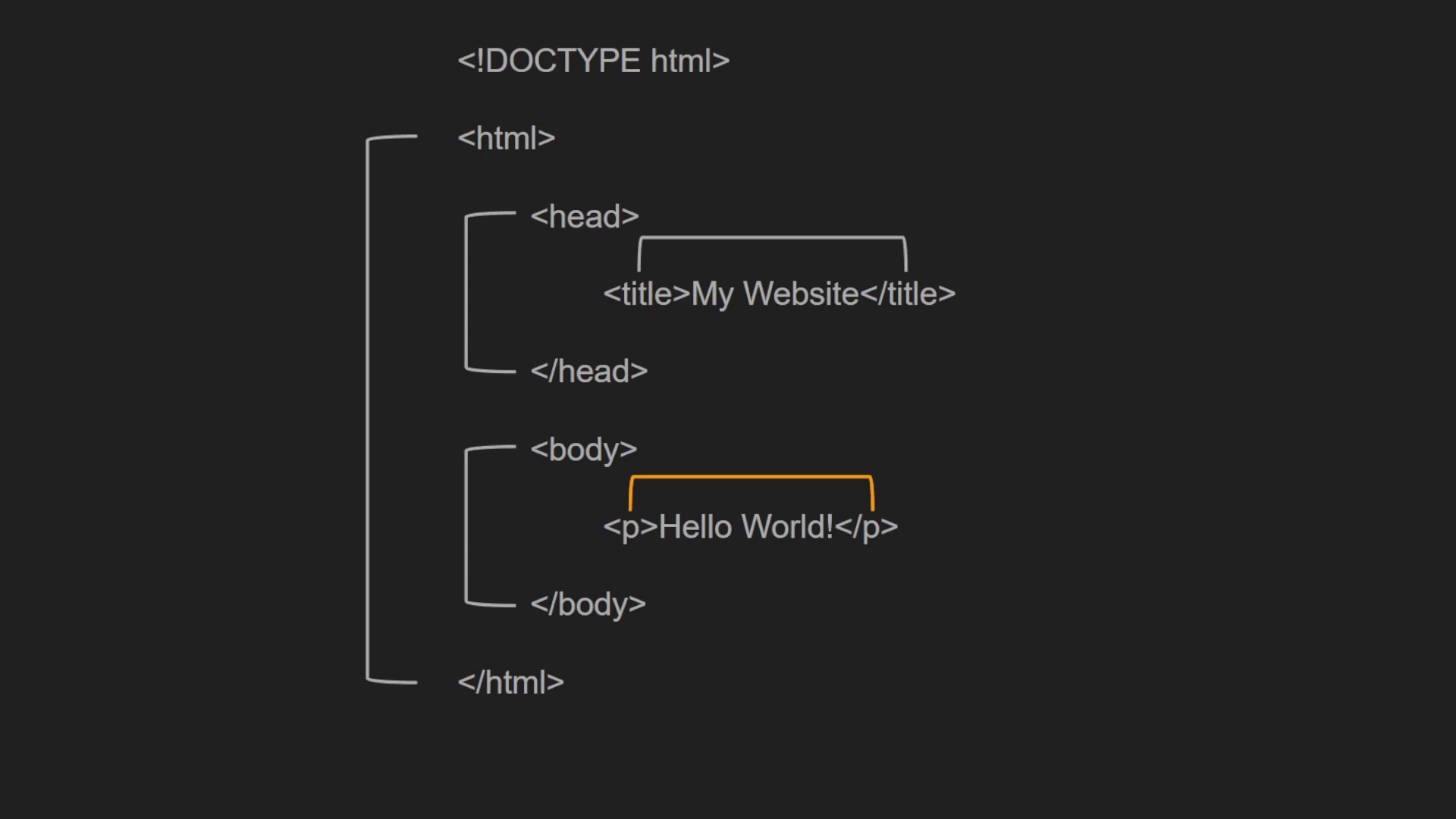
The <!DOCTYPE> tag, which specifies the type of document, is one of the first elements you will encounter when looking at an HTML template. This tag helps to prevent the browser from entering ‘quirks mode’ - an unpredictable state offering a variety of inconsistencies during rendering.
Next, we have the <html> tag, acting as a container for all other tags, barring the <!DOCTYPE>. Within the <html> tag, we encounter two other crucial elements, the <head> and <body> tags.
To draw an analogy, consider the page as a human body. The invisible metadata contained in the <head> tag represents the cognitive part, while the tangible content visible in the browser, contained in the <body> tag represents the visible physical part. In the <head> tag, we usually input details like the title, CSS and JavaScript references.
 ## Nesting of Tags
## Nesting of Tags
A point to note is the importance of right nesting in HTML. A wrongly nested set like the one shown below can screw up the page display.
 ```html
```html
Hello, world!
```The key to correctly nesting tags lies in visualizing them as quotes or parentheses. Each nested pair must be closed before the outer pair is closed. The oversight of a single forward slash / or mismatch in order can turn into a nightmare, leading to incorrect display of pages.
Here’s the correct ordering of those tags:
<body>
<p>Hello, world!<p>
</body>But don’t worry! With every mistake you make, you’ll learn something new - the language of the web awaits. Stay tuned for our next post, where we’ll dive into HTML attributes and the importance of clean code.
So until next time, keep coding and experimenting!